1/14
Why Do Muscles Grow...

Metadata
- Author: @AvrahamCooperMD on Twitter
- Full Title: 1/14
Why Do Muscles Grow... - Category: #tweets
- URL: https://twitter.com/AvrahamCooperMD/status/1345753985467224064
Highlights
- 1/14
Why do muscles grow in size after weightlifting or other types of resistance training?
The answer is both more straightforward and more complicated than I realized.
Let’s get “swol”...
#Tweetorial #MedTwitter
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 2/
First, a review of skeletal muscle physiology:
The fundamental unit of muscular contraction is the sarcomere, made up of actin and myosin proteins.
Myosin slides along actin in an ATP-dependent fashion, shortening the sarcomere, inducing contraction.
https://t.co/azqjOY77HH
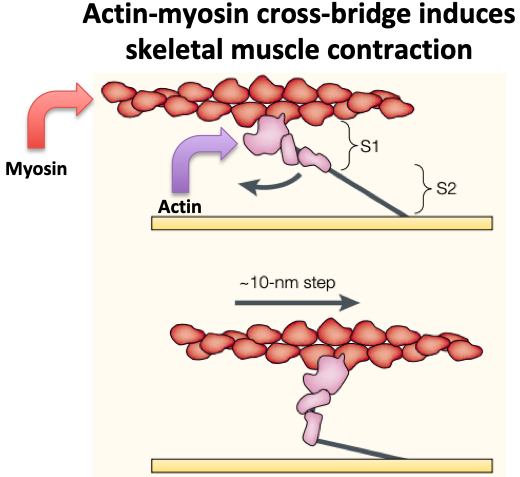 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 3/
Sarcomeres line up in parallel and are bunched into myofibrils.
Myofibrils pack together to make muscle fibers, which comprise skeletal muscle.
https://t.co/descHaZOK4
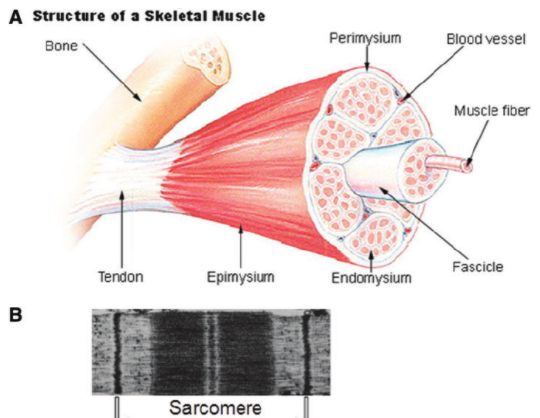 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 4/
I assumed the answer to this question was simple - hypertrophy.
But there are 3 phases to muscle growth w/ exercise:
✅ Muscle pump (immediate swelling)
✅ Inflammatory (delayed swelling, hours-days)
✅ Hypertrophy (days)
Let’s break each one down.
https://t.co/IGuanjx3nf (View Tweet) - 5/
✅ First, there is immediate swelling (within minutes of exercise).
💡Not surprisingly, blood flow to exercising muscle increases dramatically to meet metabolic demands.
https://t.co/pSQ0YLi05t
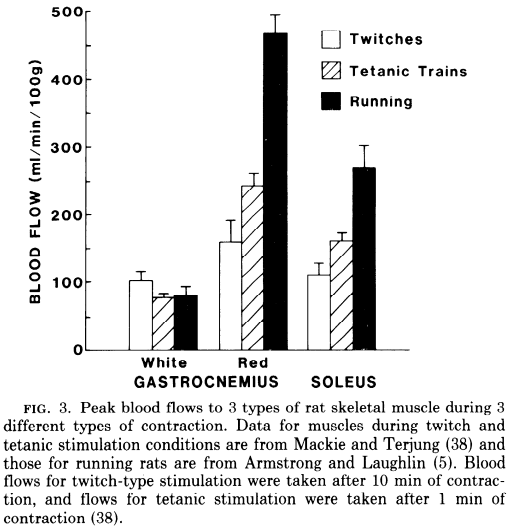 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 6/
Blood flow ⬆️ to muscle during exercise b/c of the so-called muscle pump.
Contracted muscle squeezes valved veins, pushing blood through w/ contraction and pulling in more blood w/ relaxation.
🔑This "pumped" blood flow leads to rapid swelling.
https://t.co/w81b38TFdI
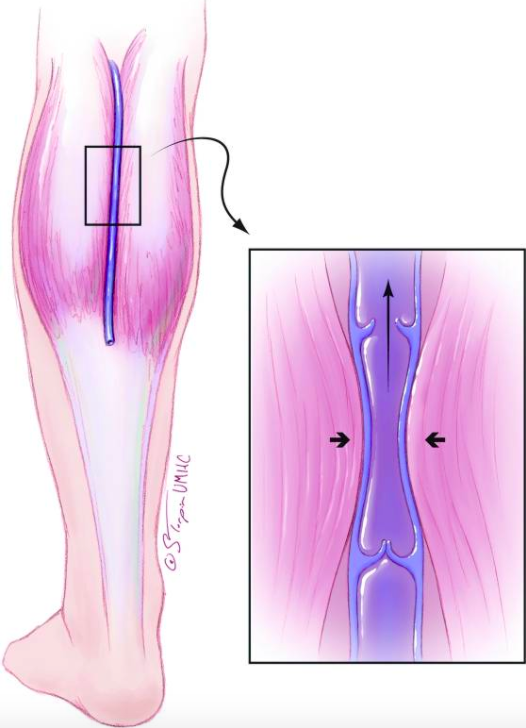 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 7/
✅ Next let's look at delayed swelling (hours-days).
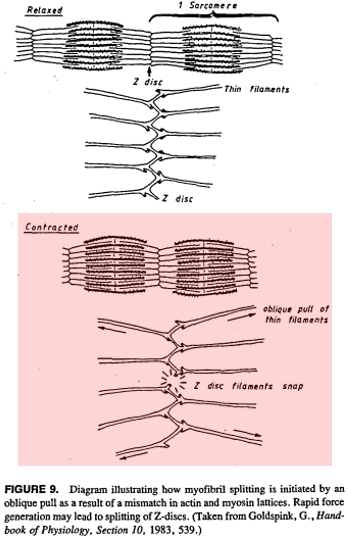
The load from weightlifting causes microdamage to sarcomeres, as actin and myosin are pulled apart w/ forced contraction.
💡This is known as myotrauma and is a normal part of resistance training.
https://t.co/JTNeciXlIq
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 8/
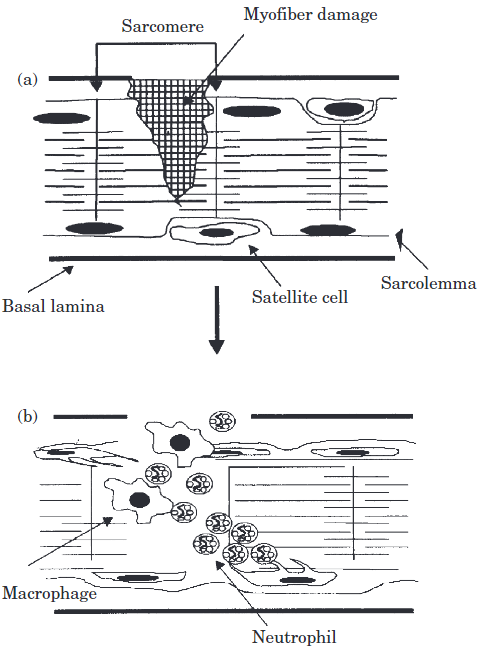
Myotrauma releases Damage Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs).
DAMPs recruit macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes into the recently-exercised muscle.
🔑Associated prostaglandin release and vasodilation causes delayed muscular swelling.
https://t.co/Ttxs8n1lf8
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 9/
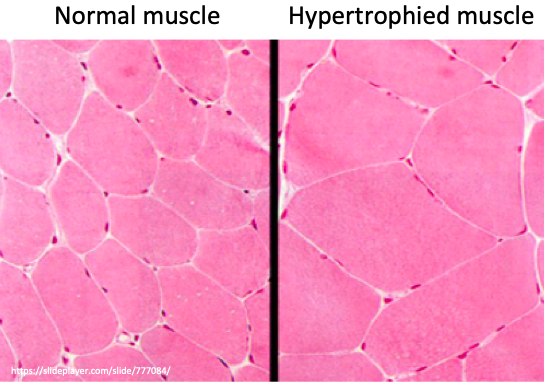
✅ The final phase, and source of longterm growth of muscle after weightlifting, is hypertrophy.
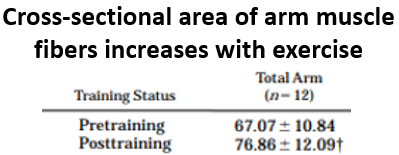
💡Studies after weight training show an increase in muscle fiber surface area without an increase in the number of fibers, consistent with hypertrophy.
https://t.co/naMYlzmnKZ
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 10/
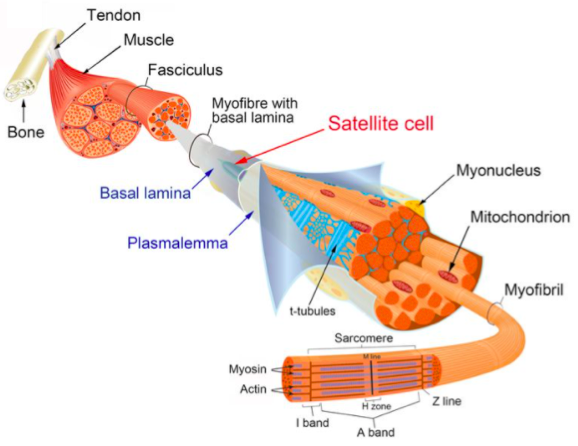
Why do muscles hypertrophy after resistance training? It has to do w/ repair of damaged fibers.
We already saw that exercise ➡️ myotrauma and macrophage recruitment.
Macrophages also activate a type of muscle stem cell called satellite cells (SC).
https://t.co/qYDGFCpWgw
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 11/
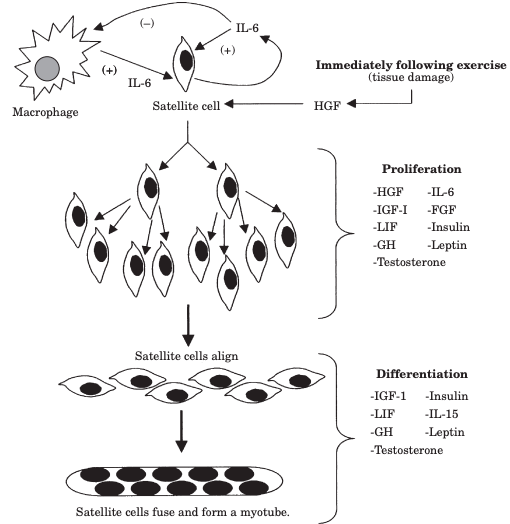
Satellite cells normally reside in a quiescent state in muscle.
⚡️Macrophages secrete IL-6, which recruits and activates them (as do circulating growth factors).
SCs then proliferate and form tube-like structures within the damaged myofibrils.
https://t.co/Ttxs8n1lf8
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 12/
Satellite cell aggregates secrete actin and myosin, which get incorporated into the damaged myofibrils, repairing and expanding them.
🔑 This leads to hypertrophy and growth of muscle in the days after exercise.
https://t.co/Ttxs8n1lf8
 (View Tweet)
(View Tweet) - 13/
In essence, we can distill down the increased size of skeletal muscle after weight training to two factors:
1⃣Increased blood flow (short term)
2⃣Repair of myotrauma (longterm) (View Tweet) - 14/
The next time you workout and your muscles grow, the following events will have occurred:
💪 Immediate swelling (increased blood flow from the muscle pump)
💪 Delayed swelling (inflammatory response to myotrauma)
💪 Hypertrophy (new protein deposition from tissue repair) (View Tweet)